


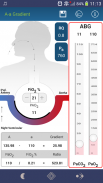


A/a Gradient

وصف لـA/a Gradient
The variables in this App. are :
RQ :Respiratory Quotient (approx 0.8 at normal physiological state)
PB : Atmospheric pressure.(760 mm Hg at sea level.)
FiO2 : Fraction of Inspired Oxygen. (0.21 at room air.)
PAO2 : Alveolar Oxygen tension
PaO2 : Arterial oxygen tension
These can be independently changed and the reflection of these changes can be seen in the alveolar – arteriolar gradient and PaO2 / FiO2 ratio.
A-a oxygen gradient : The alveolar arterial (A–a) oxygen gradient is a measure of oxygen transfer across alveolar capillary membrane (“A” denotes alveolar and “a” denotes arterial oxygenation). It is the difference between the alveolar and arterial oxygen tension.
A-a oxygen gradient = PAO2 - PaO2.
PaO2 is derived from ABG while PAO2 is calculated.
PAO2 = (FiO2 x [PB - PH2O]) - (PaCO2 ÷ RQ)
[PH2O is the partial pressure of water (47 mm Hg)] & PaCO2 is partial pressure of Carbon di oxide in arterial blood.
A-a gradient varies with age and can be estimated from the following equation, assuming the patient is breathing room air.
A-a gradient = 2.5 + 0.21 x age in years.
A-a gradient increases with higher FiO2.
PaO2/FiO2 ratio : It is a measure of Oxygen transfer across the alveolar capillary membrane. Normal PaO2/FiO2 ratio is 300 to 500 mmHg. Values less than 300 mmHg indicating impaired gas exchange and values less than 200 mmHg indicates severe hypoxemia.
"Alveolar arterial membrane is depicted in this App. as a BLACK LINE (This is purely a conceptual representation of ventilation-perfusion relationship).The thickness of this Black Line is shown to vary depending on the variations in A-a gradient"
المتغيرات في هذا التطبيق. هي:
RQ: الحاصل التنفسي (حوالي 0.8 في حالة فسيولوجية طبيعية)
PB: الضغط الجوي (760 ملم زئبق عند مستوى سطح البحر).
FiO2: جزء من الأوكسجين من وحي. (0.21 في هواء الغرفة.)
PAO2: السنخية توتر الأوكسجين
PaO2: الشرياني توتر الأوكسجين
هذه يمكن أن تتغير بشكل مستقل ويمكن رؤية انعكاس هذه التغيرات في السنخية - الانحدار تصلب ونسبة PaO2 / FiO2.
أأ التدرج الأوكسجين: والشرايين السنخية (A-أ) الأكسجين التدرج هو مقياس لنقل الأكسجين عبر غشاء الشعرية السنخية ("A" يدل على السنخية و"أ" يدل على الأوكسجين الشرياني). هذا هو الفرق بين السنخية والشرايين توتر الأوكسجين.
A-التدرج الأوكسجين = PAO2 - PaO2.
مشتق PaO2 من ABG بينما يتم احتساب PAO2.
PAO2 = (س FiO2 [PB - PH2O]) - (PaCO2 ÷ RQ)
[PH2O هو الضغط الجزئي للمياه (47 ملم زئبق)] وPaCO2 والضغط الجزئي للالكربون أكسيد دي في الدم الشرياني.
أأ التدرج يختلف مع تقدم العمر، ويمكن أن يقدر من المعادلة التالية، على افتراض أن المريض يتنفس هواء الغرفة.
A-التدرج = 2.5 + 0.21 س سن منذ سنوات.
زيادات A-التدرج مع FiO2 أعلى.
PaO2 نسبة / FiO2: وهو مقياس لنقل الأكسجين عبر غشاء الشعرية السنخية. PaO2 نسبة / FiO2 العادية هي 300 و 500 مم زئبق. قيم أقل من 300 مم زئبق مشيرا إلى ضعف في تبادل الغازات والقيم أقل من 200 مم زئبق تشير نقص الأكسجة الشديد.
"وصفت غشاء الشرايين السنخية في هذا التطبيق. كما خط أسود (وهذا هو مجرد تمثيل المفاهيمي للعلاقة التهوية التروية). وسمك هذا الخط الأسود يظهر أن تختلف تبعا للتغيرات في أأ التدرج"


























